

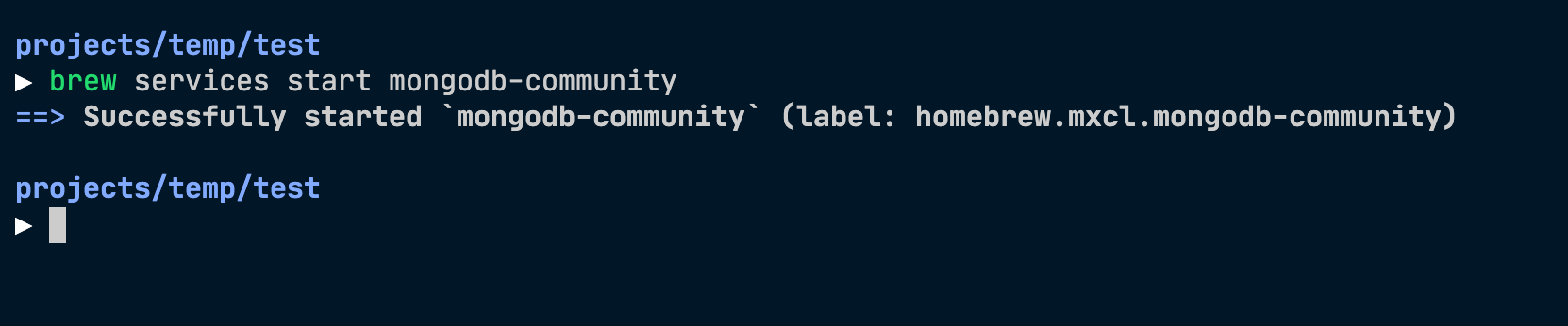
Today, you'll learn to install the MongoDB community edition on macOS Catalina and higher.
In an earlier article, I wrote about how to install the MongoDB community edition on Ubuntu operating system. create /Users/_mongod PrimaryGroupID 400 Once done, we create a new user (we use the same id as we did for the group) - no shell is needed for daemon users: $ sudo dscl. create /Groups/_mongod PrimaryGroupID 400 Please note, on OS X, by convention, all daemon users are prefixed with an underscore, such as _daemon.īefore creating a user, we create a group choosing an unused group id: # Create _mongod group Therefore, here we will use 400 (make sure it is not taken). list /Groups PrimaryGroupID | tr -s ' ' | sort -n -t ' ' -k2,2 $ dscacheutil -q group | grep gid | tail -n 1 Get the last used GID: # Get the last used GID We never want to run as super user but create a special daemon _mongod for this. # MongoDB export PATH= "/usr/local/mongodb/bin: $PATH " 4. # in replica set configuration, specify the name of the replica set # Slave only: specify a single database to replicate # in master/slave replicated mongo databases, specify here whether # Ping interval for Mongo monitoring server.


# Server name for Mongo monitoring server. # Accout token for Mongo monitoring server. Any query that would do a table scan fails. # Disable the HTTP interface (Defaults to localhost:28017). # Inspect all client data for validity on receipt (useful for # Enables periodic logging of CPU utilization and I/O wait # e.g., if the parent directory isn't mutable by the mongodb user. # need to create and set permissions for this directory manually, # Note: if you run mongodb as a non-root user (recommended) you may


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
